A quality management system is a system that includes technical, organizational, informational, human, material and financial elements. Interaction and collaboration of it is a difficult and complex task. QMS automation allows you to make this process predictable and orderly.
QMS automation
The QMS implementation purpose is to increase the stability of work. The required level of quality products or services is achieved by the stability of work. Most companies use "manual" management. They can achieve their goals and meet the quality system requirements, but even well-established "manual" processes cannot be eliminated from disadvantages - low productivity and human error.
It is necessary to produce high-quality products (services) quickly and at a low price in order to be competitive. The cost is reduced, the quality is improved, the work cycle is shortened, productivity and work efficiency are increased due to the automation of the QMS.
QMS automation directions
QMS automation includes three directions. Each of them depends on the quality system integration into the company's work. Automation can be vertically (hierarchical management levels), horizontally (by processes) and by functionality (between subsystems).
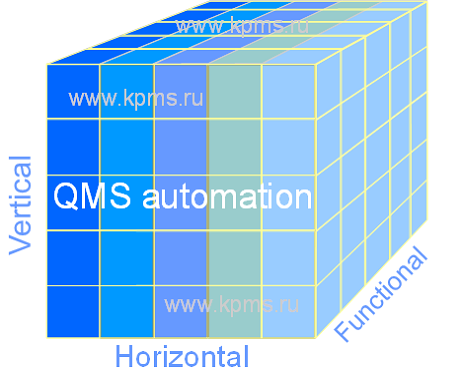
- The vertical direction of QMS automation includes hierarchical levels: strategic, tactical and operational. The automation task in this direction is to ensure the stability of the control elements interaction. The control elements are understood as: information, organizational units, communication channels, management decisions.
- The horizontal direction is focused on the life cycle processes automation of a product or service. It includes production and related processes. The QMS automation task for this direction is to ensure stable productivity and efficiency of processes.
- The functional direction of QMS automation includes management subsystems (planning, production, supply, document management, etc.). The task of automation is to ensure the completeness, validity and reliability of data transmission.
QMS automation objects
The ISO 9001:2015 standard requirements include many aspects of the organization's work, so the quality system automation should be comprehensive. It must be carried out in all directions: vertical, horizontal and functional. Each direction of QMS automation has its own objects.
The automation object is always an activity. Any activity includes two components: object transformation and restrictions on transformations. The direction of QMS automation will change and the object will be specified depending on the type of activity.
The vertical direction is the automation of management decisions. It is necessary to initiate a control action, get feedback from the managed link, compare the results with the established criteria and make adjustments in order to develop, adopt and implement management decisions.
The QMS automation objects will be in this case:
- goals and objectives set. They can be set at different levels. The goals are detailed to the level of tasks when they are deployed. Various planning options (strategic planning, activity planning, operational planning, etc.) are used as a tool;
- responsibilities and powers distribution. It is necessary to identify responsible persons in order to perform tasks (achieve goals). Responsibilities and powers determine the role of personnel in the QMS. Various organizational structures, responsibility matrices, assignment of tasks, etc. can be used as a tool;
- data analysis and processing. There is a different level of data detailing and methods of processing them. Statistical methods, data structuring methods, sampling, etc. can be used as a tool;
- management levels interactions. These actions involve the transfer of objects (usually information) between management levels. Information routing, task escalation, data publication, etc. are used as interaction tools.
The horizontal direction is the actions automation in processes. Actions can be performed if there are strictly specified conditions and parameters of operation only. They will lead to the expected result in this case.
The QMS automation objects will be:
- operations and process transitions performing. Each process operation (transition) has a set of attributes: execution time, processing object, resources involved, cost, etc. These attributes define the requirements for the automation tools selection;
- information and data transformation that accompanying the process. Each operation is accompanied by data (reference, technological, control, etc.) in the process. The data change confirms the operation. Data collection is necessary for making management decisions and analyzing the process work;
- interactions between operations within the process. The operations of the process are interdependent. They can be executed either sequentially or in parallel. Interactions are carried out through the material or information objects transfer. The objects transfer must be synchronized for the stable execution of the process.
The functional direction is automation of subsystems organization interaction. The interaction between processes also belongs to this direction. Subsystems can interact by exchanging objects (material and informational).
The QMS automation objects will be in this case:
- interactions between subsystems. The organization may have subsystems: production, warehouse, supply, document management, etc. These subsystems interact with each other through elements (interaction of personnel, material and information flows, work flows, etc.). Interactions should be regulated for stable operation;
- interactions between processes. The organization's processes are interrelated. The actions execution of one process affects the result of work in another process. Such impacts can be stretched over time. QMS automation should take into account the impact of processes on each other;
- interactions between management levels. Information and data are transferred between the management levels. The reliability of information is the basis of managerial decision-making.
QMS automation tools
The complexity and diversity of the quality system requirements does not allow to automate the QMS through the use of the only software tool. The only tool can partially solve problem although many automation system developers claim that their products meet all the requirements of ISO 9001.
Different directions and objects of QMS automation make the use of different products. Complex automation is possible only through the integration of several systems.
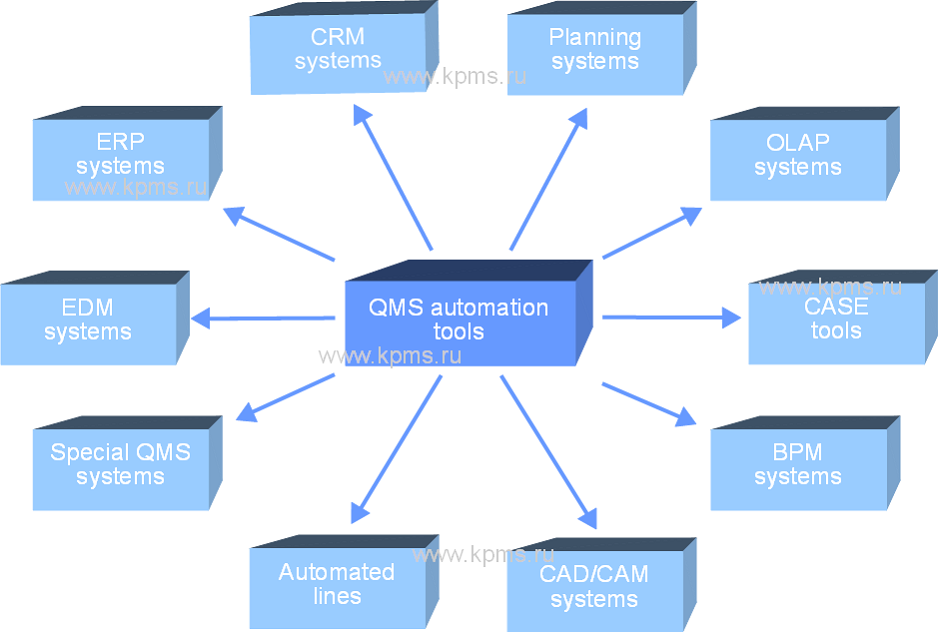
A functional direction is chosen most often for automating the QMS, because it is "understandable" for the organization's employees and quality specialists. Automation tools implement part of the quality system functions related to the processing and transmission of information and data.
Such tools include:
- CRM systems. They automate the transmission and processing of information related to customers and external parties. It is possible to implement only part of the quality system requirements due to these software tools. The use of CRM in QMS has many limitations;
- ERP systems. These systems automate the quality system elements related to production processes: production management, procurement, sales, service, etc. The execution of processes is not automated. These systems only transform and transmit information about processes;
- EDM systems (electronic document management systems). They make it possible to automate the documentation and data management. The information comes from other subsystems (ERP systems, CRM systems) or is entered manually;
- special QMS systems. They are created specifically for the quality system elements automation, but their capabilities are limited. They allow you to manage part of the information on individual issues of the quality system: QMS audits, documentation, work plans.
Other systems and complexes are used to automate the execution of processes (the horizontal direction):
- automated lines and equipment. These are production complexes or robotic lines that are capable of performing production operations according to a given program. They are used for automation of production and measurement processes and belong to the lower level of automation;
- CAD\CAM systems. They are used to automate design processes. They are based CALS technologies and allow you to automatically perform various stages of project development;
- BPM systems. This type of automation systems can be called as the process type. They are suitable to automate business processes. These systems cannot fully perform business processes in automatic mode, but they allow automating a significant part of management operations;
- CASE – tools. It is suitable for process design. It is possible to automate a significant part of the operations for developing the order and conditions for the execution of processes with the help of these systems.
The vertical direction of QMS automation can be implemented by:
- OLAP – systems. They automate the analysis and processing of data at different levels of management. It is necessary to ensure data collection for the system to work, because OLAP systems can only process information;
- planning systems. These systems ensure the setting of goals and objectives, control of their execution, escalation of tasks and monitoring of the achievement of goals.
The system composition can be expanded through the use of specialized tools (billing systems, POS systems, Help Desk systems, etc.) depending on the field of activity of the organization.
It is carried out integration of various systems in order to implement the integrated automation of the QMS. The choice of their composition is determined by the current processes and the needs of the organization. It is important to understand that it is impossible to automate the fulfillment of all the requirements of the quality system by using one system.
