The use of the OLAP system allows you to automate the strategic level of organization management. OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) is a powerful technology for data processing and research. OLAP systems provide almost limitless opportunities for compiling reports, performing complex analytical calculations, making forecasts and scenarios, and developing a variety of plan options.
OLAP systems
Full-fledged OLAP systems appeared in the early 90s as a result of the development of decision support information systems. They are designed to convert various data (often disparate) into useful information. OLAP systems can organize data according to a certain set of criteria. It is not necessary that the criteria have clear characteristics.
OLAP systems have found their application in many issues of strategic management of the organization: business performance management, strategic planning, budgeting, development forecasting, preparation of financial statements, work analysis, simulation of the external and internal environment of the organization, data storage and reporting.
OLAP system structure
The OLAP system is based on the processing of multidimensional data arrays. Each element of the multidimensional arrays has many connections with other elements. The OLAP system must receive source data from other systems (for example, ERP or CRM systems) or through external input in order to form a multidimensional array. The OLAP system user receives the necessary data in a structured form in accordance with his request. You can imagine the structure of the OLAP system based on the specified procedure.
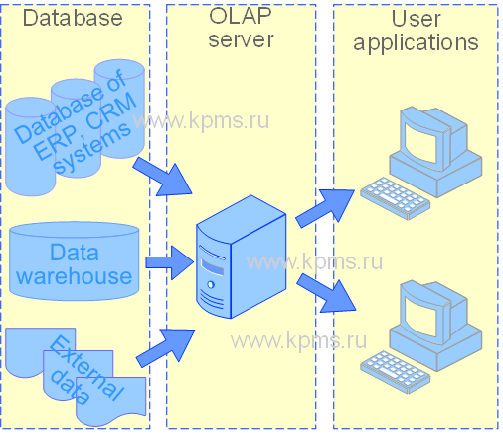
The structure of the OLAP system consists of the following elements:
- database. The database is a source of information for the OLAP system operation. The database type depends on the OLAP system type and the algorithms of the OLAP server. As a rule, it is used relational databases, multidimensional databases, data warehouses, etc.
- OLAP server. It provides management of the multidimensional data structure and the relationship between the database and the users of the OLAP system.
- custom applications. This element of the OLAP system structure manages user requests and generates the results of accessing the database (reports, graphs, tables, etc.).
OLAP systems can be implemented on users' local computers or using dedicated servers depending on the way data is organized, processed and stored.
There are three main ways to store and process data:
- locally. The data is placed on users' computers. Data processing, analysis and management are performed at local workstations. Such an OLAP system structure has significant disadvantages related to data processing speed, data security and limited use of multidimensional analysis.
- relational databases. These databases are used when the OLAP system works together with a CRM system or an ERP system. Data is stored on the server of these systems in the form of relational databases or data warehouses. The OLAP server accesses these databases to form the necessary multidimensional structures and perform analysis.
- multidimensional databases. The data is organized as a special data warehouse on a dedicated server in this case. All data operations are performed on this server, which converts the source data into multidimensional structures. Such structures are called OLAP cubes. The data sources for forming an OLAP cube are relational databases and/or client files. The data server performs preliminary preparation and processing of data. The OLAP server works with an OLAP cube without having direct access to data sources (relational databases, client files, etc.).
OLAP systems types
All OLAP systems can be divided into three main types depending on the method of data storage and processing.
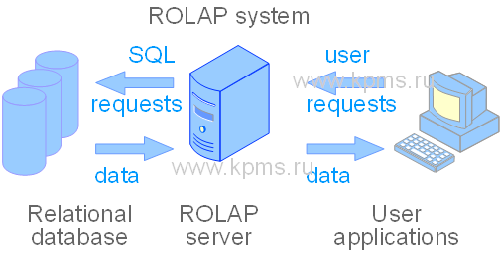
1. ROLAP (relational OLAP systems) – this type of OLAP system works with relational databases. The data gives from a relational database. The data is stored as relational tables. Users have the ability to perform multidimensional analysis as in traditional OLAP systems. This is achieved through the use of SQL tools and special queries.
One of the advantages of ROLAP system is the ability to process large amounts of data more efficiently. Another advantage of ROLAP is the ability to efficiently process both numeric and textual data.
The disadvantages of ROLAP is low performance (compared to traditional OLAP systems), since data processing is carried out by the OLAP server. Another disadvantage is the limitation of functionality due to the use of SQL.
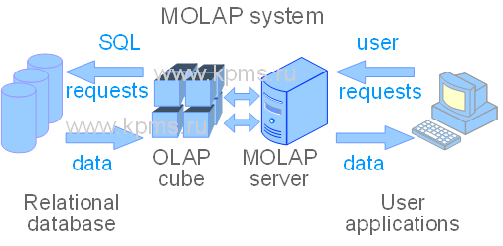
2. MOLAP (multidimensional OLAP systems). This type of OLAP systems is to traditional systems. The difference between a traditional OLAP system and other systems is the preliminary preparation and optimization of data. As a rule, these systems use a dedicated server on which data is preprocessed. The data is formed into multidimensional arrays – OLAP cubes.
MOLAP systems are the most efficient in data processing, because they make it easy to reorganize and structure data for various user requests. MOLAP analytical tools allow you to perform complex calculations. Another advantage of MOLAP is the ability to quickly generate queries and get results. This is provided by the preliminary formation of OLAP cubes.
The disadvantages of the MOLAP system is the limitation of the volume of processed data and data redundancy, because data has to be duplicated for the formation of multidimensional cubes.
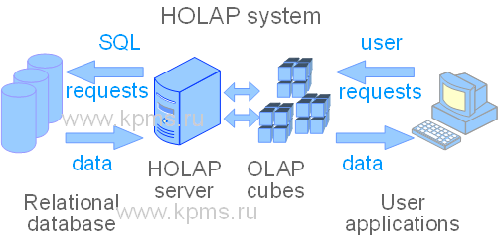
3. HOLAP (hybrid OLAP systems). Hybrid OLAP systems are a combination of ROLAP and MOLAP systems. It has tried to combine in hybrid systems the advantages of two systems: the use of multidimensional databases and relational database management. HOLAP systems allow you to store a large amount of data in relational tables, and the processed data is placed in pre-built multidimensional OLAP cubes. The advantages of this systems type are data scalability, fast data processing and flexible access to data sources.
There are other types of OLAP systems, but they are a marketing ploy of manufacturers than an independent type of OLAP system.
These types include:
- WOLAP (Web OLAP). This is a type an OLAP system with web interface support. It is possible to access databases via the web interface in these OLAP systems.
- DOLAP (Desktop OLAP). This type of OLAP system allows users to upload a database to a local workplace and work with it locally.
- MobileOLAP. This is a feature of OLAP systems that allows you to work with the database remotely by using mobile devices.
- SOLAP (Spatial OLAP). This type of OLAP systems is designed for processing spatial data. It appeared as a result of the integration of geographic information systems and OLAP systems. These systems allow processing data not only in alphanumeric format, but also in the form of visual objects and vectors.
OLAP systems Advantages
The use of the OLAP system gives the organization the ability to predict and analyze various situations related to current activities and development prospects. These systems can be considered as an addition to enterprise-level automation systems. All the advantages of OLAP systems directly depend on the accuracy, reliability and volume of the source data.
The main advantages of the OLAP system are:
- consistency of the initial information and the results of the analysis. It is always possible to trace the source of information and determine the logical relationship between the results obtained and the source data in the presence of an OLAP system. The subjectivity of the analysis results is reduced.
- multivariate analysis conducting. The use of the OLAP system allows you to obtain a variety of scenarios for the development of events based on a set of source data. It is possible to simulate situations on the principle of "what will happen if" due to the analysis tools.
- detail management. The detail of the results presentation may vary depending on the needs of users. There is no need to carry out complex system settings and repeat calculations at the same time. The report may contain the information that is necessary for decision-making.
- identification of hidden dependencies. It becomes possible to find and identify hidden dependencies in various processes or situations that affect production activities due to the construction of multidimensional relationships.
- creating a single platform. It becomes possible to create a single platform for all forecasting and analysis processes in the enterprise due to the use of the OLAP system. In particular, the data of the OLAP system are the basis for making budget forecasts, sales forecasts, procurement forecasts, strategic development plans, etc.
